9.28 读写分离/主从复制
9.28.1 读写分离
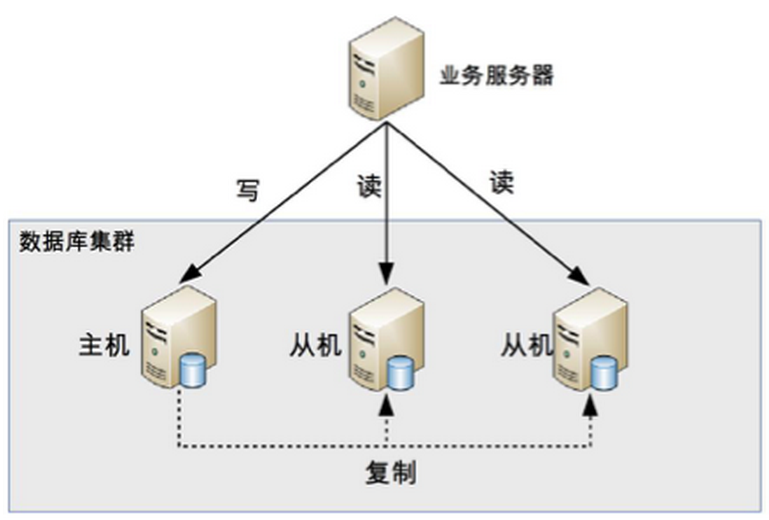
其实就是将数据库分为了主从库,一个主库用于写数据,多个从库完成读数据的操作,主从库之间通过某种机制进行数据的同步,是一种常见的数据库架构。
9.28.1.1 解决了什么问题
大多数互联网业务,往往读多写少,这时候,数据库的读会首先成为数据库的瓶颈,这时,如果我们希望能够线性的提升数据库的读性能,消除读写锁冲突从而提升数据库的写性能,那么就可以使用“分组架构”(读写分离架构)。
用一句话概括,读写分离是用来解决数据库的读性能瓶颈的。
9.28.1.2 注意事项
- 数据库连接池要进行区分,哪些是读连接池,哪个是写连接池,研发的难度会增加;
- 为了保证高可用,读连接池要能够实现故障自动转移;
- 主从的一致性问题需要考虑。
9.28.2 如何实现
Furion 在数据库模块设计之初,就考虑了读写分离这种情况,所以从底层就支持动态切换数据库上下文及读写操作方法约束。
读写分离操作主要使用 IMSRepository 仓储,该仓储已经为开发者提供方便的操作调用。当然也可以不使用该仓储。
下面就给大家演示如何读写多库读写操作。
9.28.2.1 创建 主库 数据库上下文
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Furion.EntityFramework.Core
{
/// <summary>
/// 主库数据库上下文
/// </summary>
[AppDbContext("MasterConnectionString")]
public class MasterDbContext : AppDbContext<MasterDbContext>
{
public MasterDbContext(DbContextOptions<MasterDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
}
}
数据库连接字符串:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"MasterConnectionString": "Server=localhost;Database=Furion;User=sa;Password=000000;MultipleActiveResultSets=True;"
}
}
9.28.2.2 创建 从库 数据库上下文
using Furion.Core;
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Furion.EntityFramework.Core
{
/// <summary>
/// 从库数据库上下文
/// </summary>
[AppDbContext("SlaveConnectionString")]
public class SlaveDbContext : AppDbContext<SlaveDbContext, SlaveDbContextLocator>
{
public SlaveDbContext(DbContextOptions<SlaveDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
}
}
多数据库操作除了默认数据库无需自定义 数据库上下文定位器,其他数据库都需要有数据库上下文定位器。如 SlaveDbContextLocator
从库数据库上下文定位器:
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
namespace Furion.Core
{
/// <summary>
/// 从库数据库上下文定位器
/// </summary>
public class SlaveDbContextLocator : IDbContextLocator
{
}
}
数据库连接字符串:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"SlaveConnectionString": "Server=localhost;Database=FurSlave;User=sa;Password=000000;MultipleActiveResultSets=True;"
}
}
9.28.2.3 注册 主从库 数据库上下文
using Furion.Core;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace Furion.EntityFramework.Core
{
[AppStartup(600)]
public sealed class FurEntityFrameworkCoreStartup : AppStartup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDatabaseAccessor(options =>
{
services.AddDbPool<MasterDbContext>();
services.AddDbPool<SlaveDbContext, SlaveDbContextLocator>();
});
}
}
}
9.28.2.4 创建 Person 实体
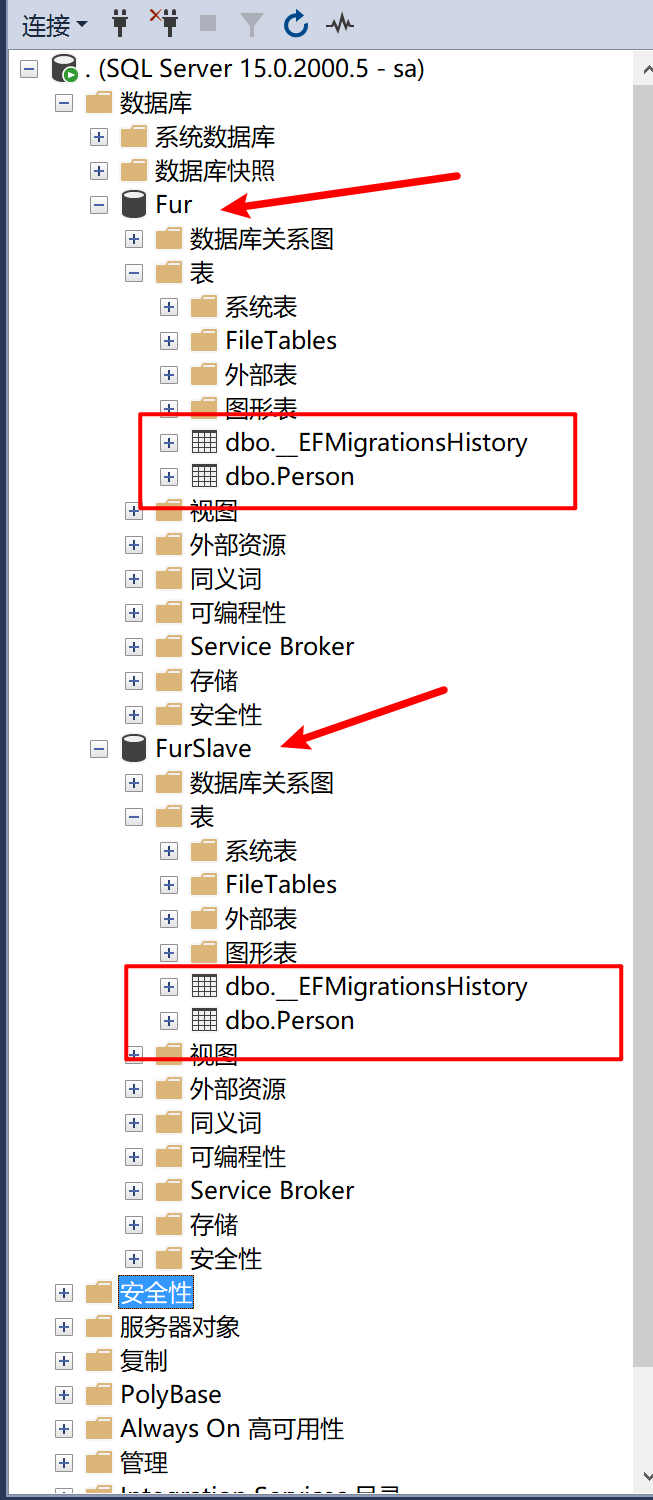
由于 主从库 具有相同的数据库结构,所以实体也必须声明 主从库:
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace Furion.Core
{
public class Person : IEntity<MasterDbContextLocator, SlaveDbContextLocator>
{
/// <summary>
/// 主键Id
/// </summary>
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 名称
/// </summary>
public string Name { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 年龄
/// </summary>
public int Age { get; set; }
}
}
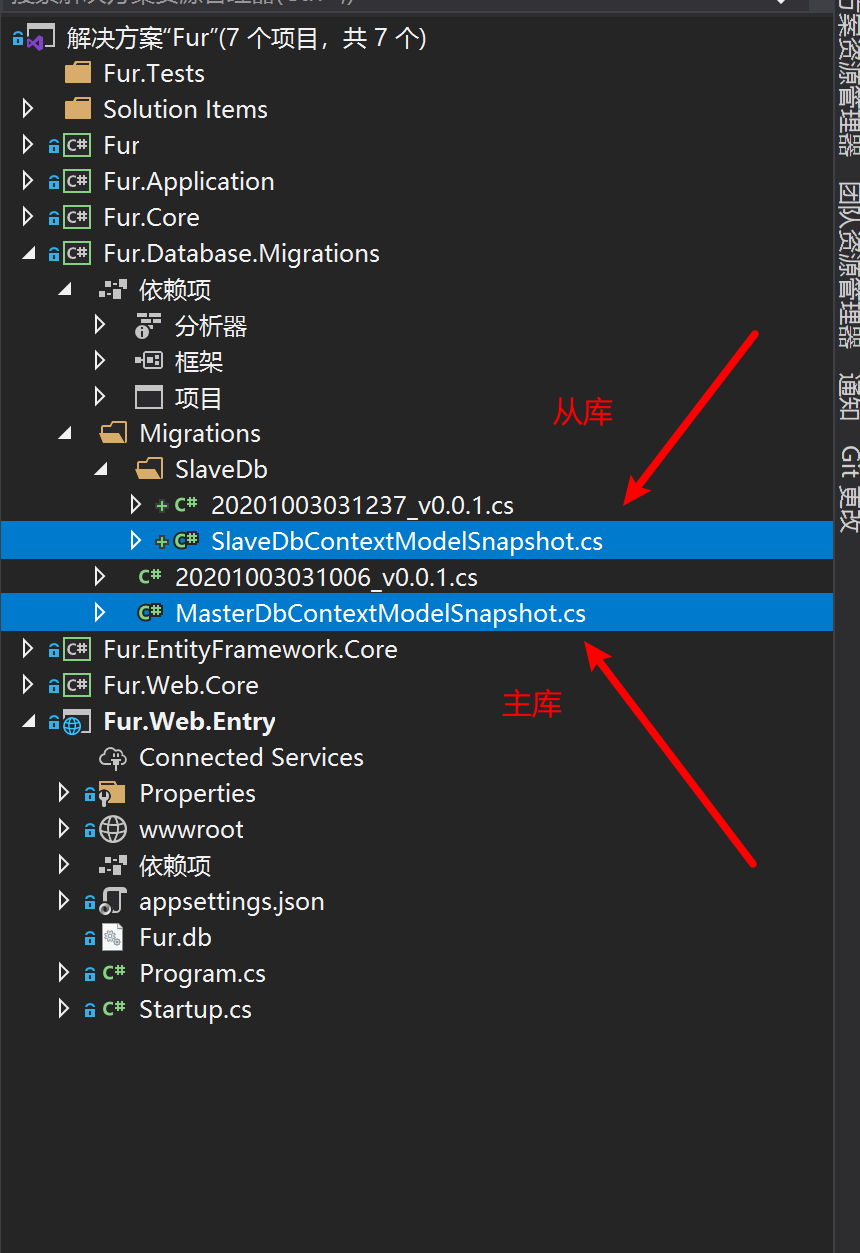
9.28.2.5 将 Person 转换成数据库表
创建主库数据库表:
Add-Migration v0.0.1 -Context MasterDbContext
Update-Database -Context MasterDbContext
创建从库数据库表:
Add-Migration v0.0.1 -Context SlaveDbContext
Update-Database -Context SlaveDbContext
9.28.2.6 固定主从库使用例子
using Furion.Core;
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using Furion.DynamicApiController;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Furion.Application
{
public class PersonService : IDynamicApiController
{
/// <summary>
/// 可调配仓储(读写分离)
/// </summary>
private readonly IMSRepository<MasterDbContextLocator, SlaveDbContextLocator> _msRepository;
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数初始化
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msRepository"></param>
public PersonService(IMSRepository<MasterDbContextLocator, SlaveDbContextLocator> msRepository)
{
_msRepository = msRepository;
}
/// <summary>
/// 新增走主库
/// </summary>
/// <param name="person"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public void Insert(Person person)
{
_msRepository.Master<Person>().Insert(person);
}
/// <summary>
/// 查询走从库
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<Person> Get()
{
return _msRepository.Slave1<Person>().AsEnumerable().ToList();
}
}
}
9.28.2.7 随机或 自定义返回从库 ✨
在 Furion 2.4.1 + 版本新增了 IMSRepository 和 IMSRepository<TMasterDbContextLocator> 仓储类型,可以获取随机仓储或自定义仓储。使用例子如下:
- 配置 主库
[AppDbContext]特性的SlaveDbContextLocators属性,可通过构造函数最后参数传入,如:
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Furion.EntityFramework.Core
{
[AppDbContext("Sqlite3ConnectionString", DbProvider.Sqlite, typeof(从库定位器1), typeof(从库定位器2), typeof(从库定位器3))]
public class MasterDbContext : AppDbContext<MasterDbContext>
{
public MasterDbContext(DbContextOptions<MasterDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
}
}
- 使用
IMSRepository或IMSRepository<TMasterDbContextLocator>
using Furion.Core;
using Furion.DatabaseAccessor;
using Furion.DynamicApiController;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Furion.Application
{
public class PersonService : IDynamicApiController
{
/// <summary>
/// 可调配仓储(读写分离)
/// </summary>
private readonly IMSRepository _msRepository; // 不指定定位器,默认是 MasterDbContextLocator
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数初始化
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msRepository"></param>
public PersonService(IMSRepository msRepository)
{
_msRepository = msRepository;
}
/// <summary>
/// 新增走主库
/// </summary>
/// <param name="person"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public void Insert(Person person)
{
_msRepository.Master<Person>().Insert(person);
}
/// <summary>
/// 随机从库
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<Person> Get()
{
return _msRepository.Slave<Person>().AsEnumerable().ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// 自定义从库
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<Person> Get()
{
return _msRepository.Slave<Person>(() => {
// 这里写你的逻辑返回从库定位器
return 你的从库定位器;
}).AsEnumerable().ToList();
}
}
}
IMSRepository 不带泛型默认指的是 IMSRepository<TMasterDbContextLocator>,如需泛型版本,则使用 IMSRepository<定位器>
9.28.3 主从复制
主从复制:是一种数据备份的方案。
简单来说,是使用两个或两个以上相同的数据库,将一个数据库当做主数据库,而另一个数据库当做从数据库。在主数据库中进行相应操作时,从数据库记录下所有主数据库的操作,使其二者一模一样。
9.28.4 主从复制几种方式
9.28.4.1 同步复制
所谓的同步复制,意思是 Master 的变化,必须等待 Slave-1,Slave-2,...,Slave-n 完成后才能返回。
这样,显然不可取,比如,在 Web 前端页面上,用户增加了条记录,需要等待很长时间。
9.28.4.2 异步复制
如同 AJAX 请求一样。Master 只需要完成自己的数据库操作即可。至于 Slaves 是否收到二进制日志,是否完成操作,不用关心。(推荐方式)
9.28.4.3 半同步复制
Master 只��保证 Slaves 中的一个操作成功,就返回,其他 Slave 不管。
下面将使用 SqlServer 简单配置主从复制功能。
9.28.5 SqlServer 主库配置
9.28.5.1 添加 本地发布
9.28.5.2 选择 分发服务器
9.28.5.3 启用 代理
9.28.5.4 发布数据库
9.28.5.5 快照发布
具体��选择何种发布类型,视具体业务场景而定。
9.28.5.6 选择发布项目
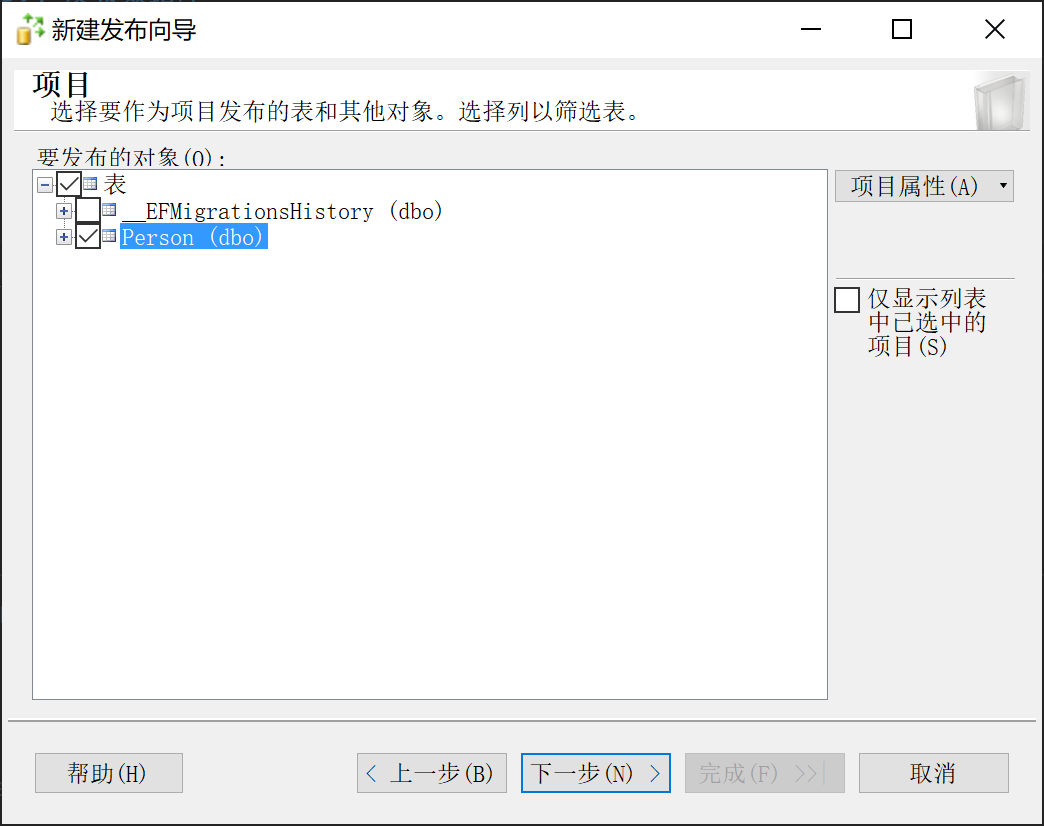
9.28.5.7 配置分发计划
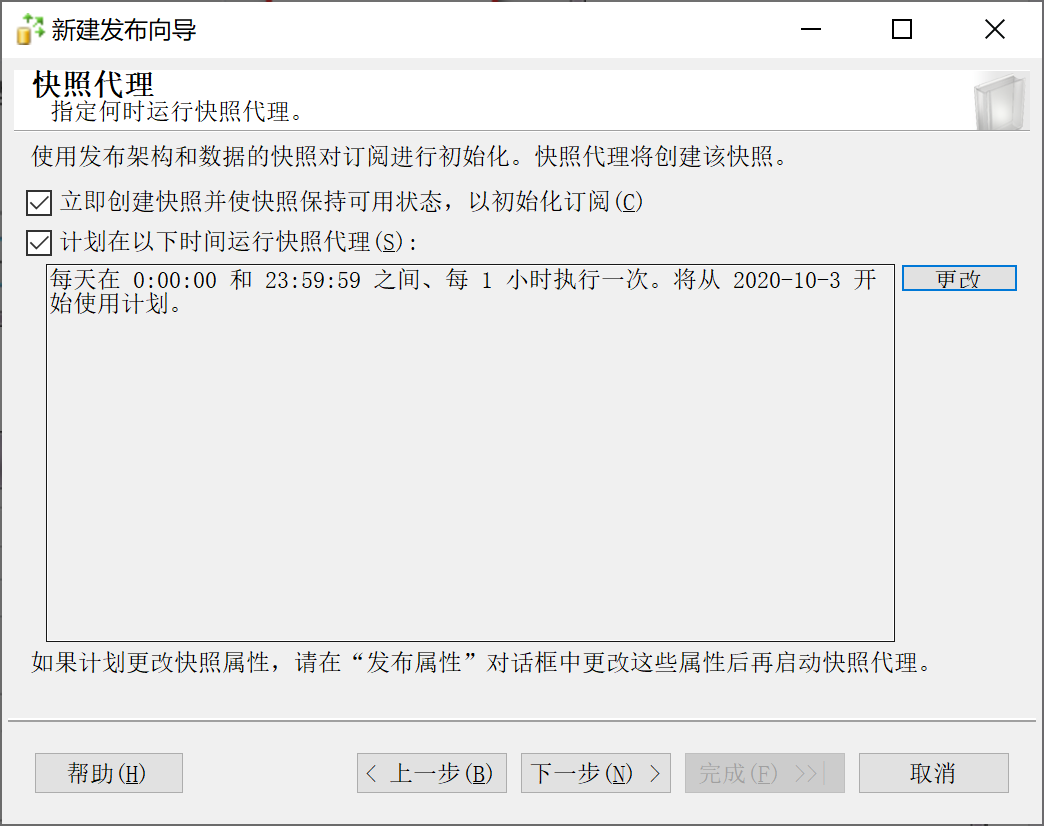
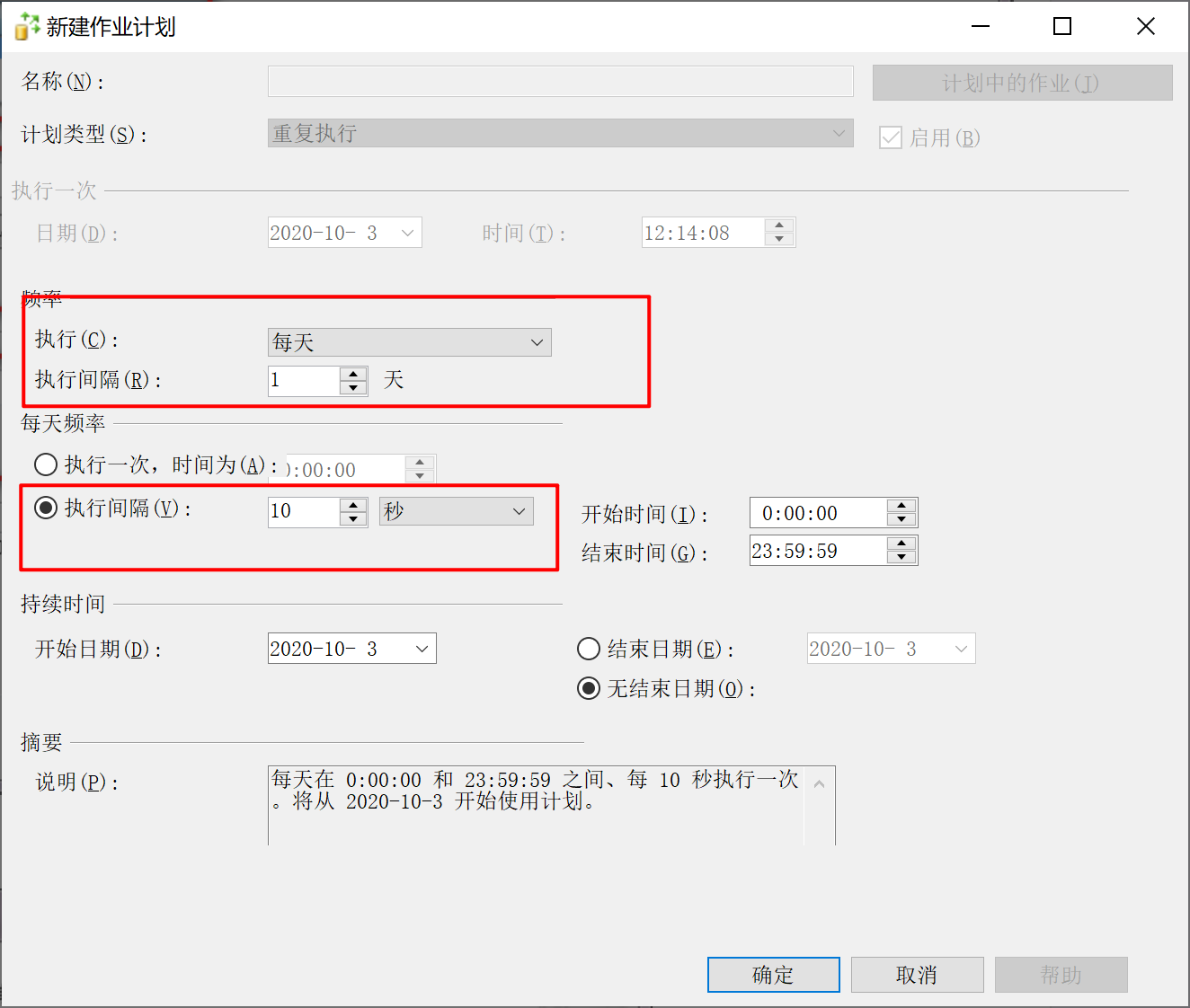
9.28.5.8 配置安全设置
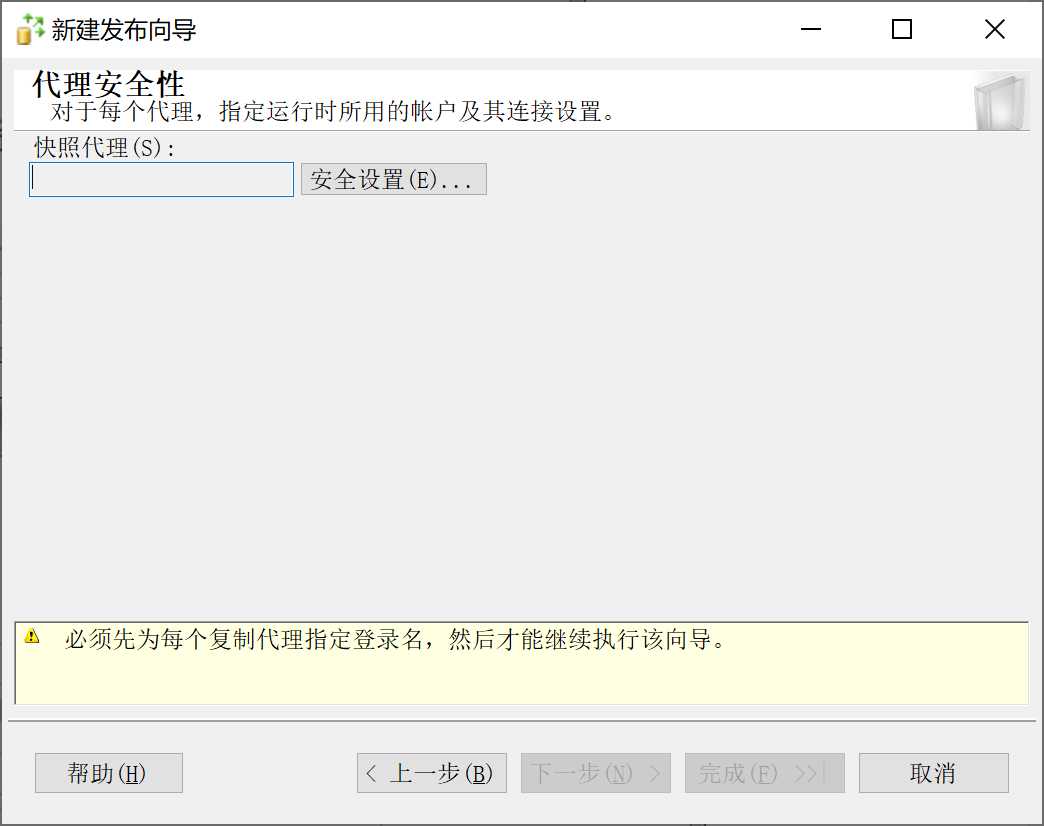
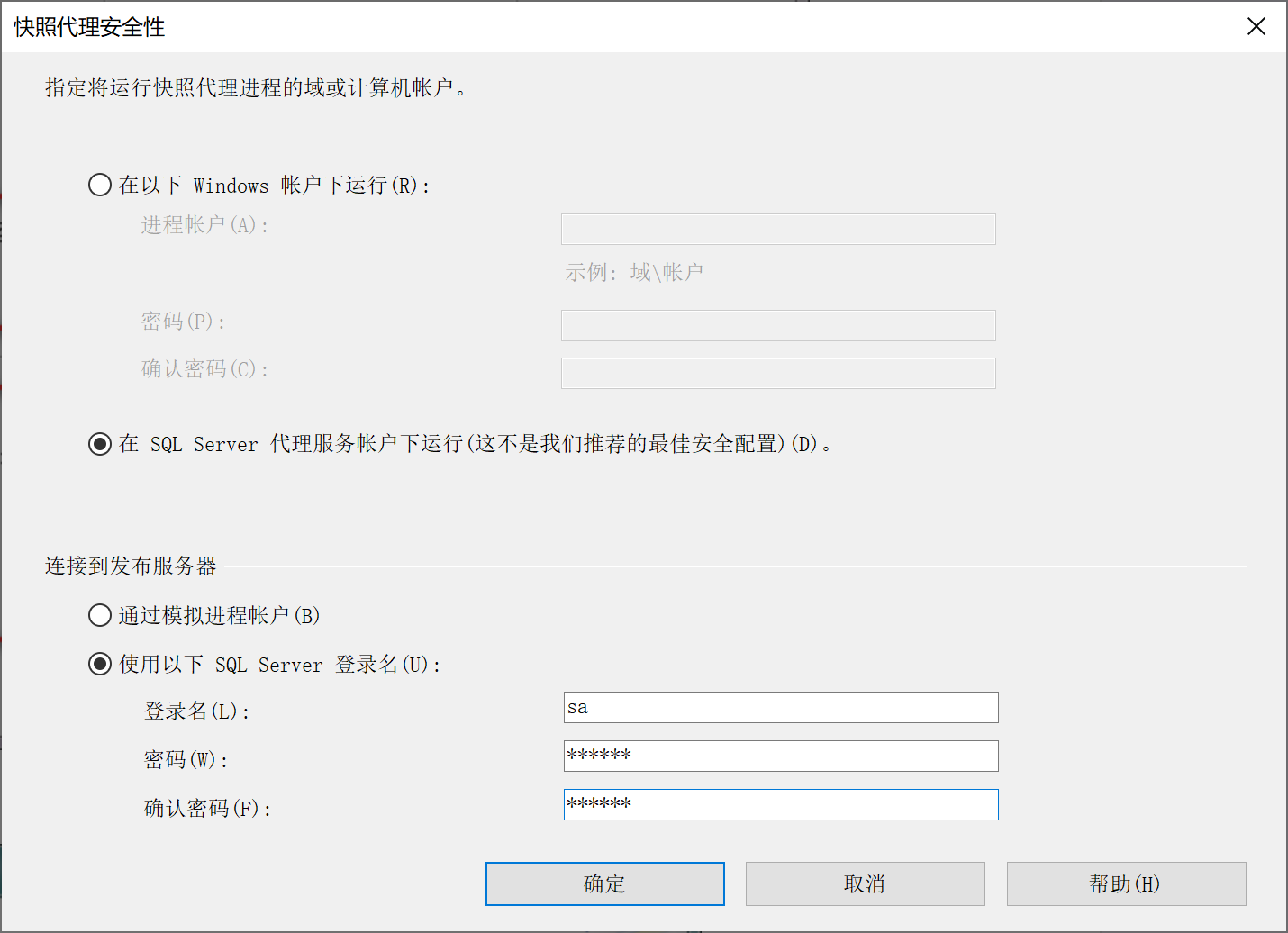
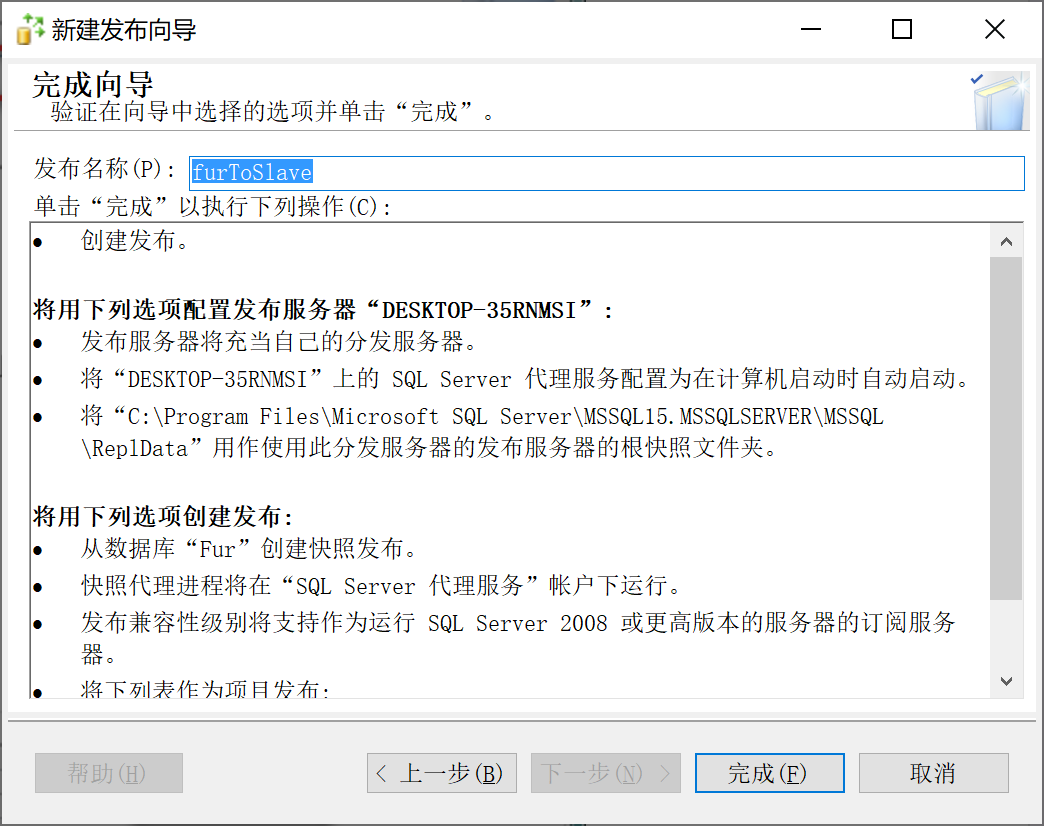
9.28.5.9 完成配置
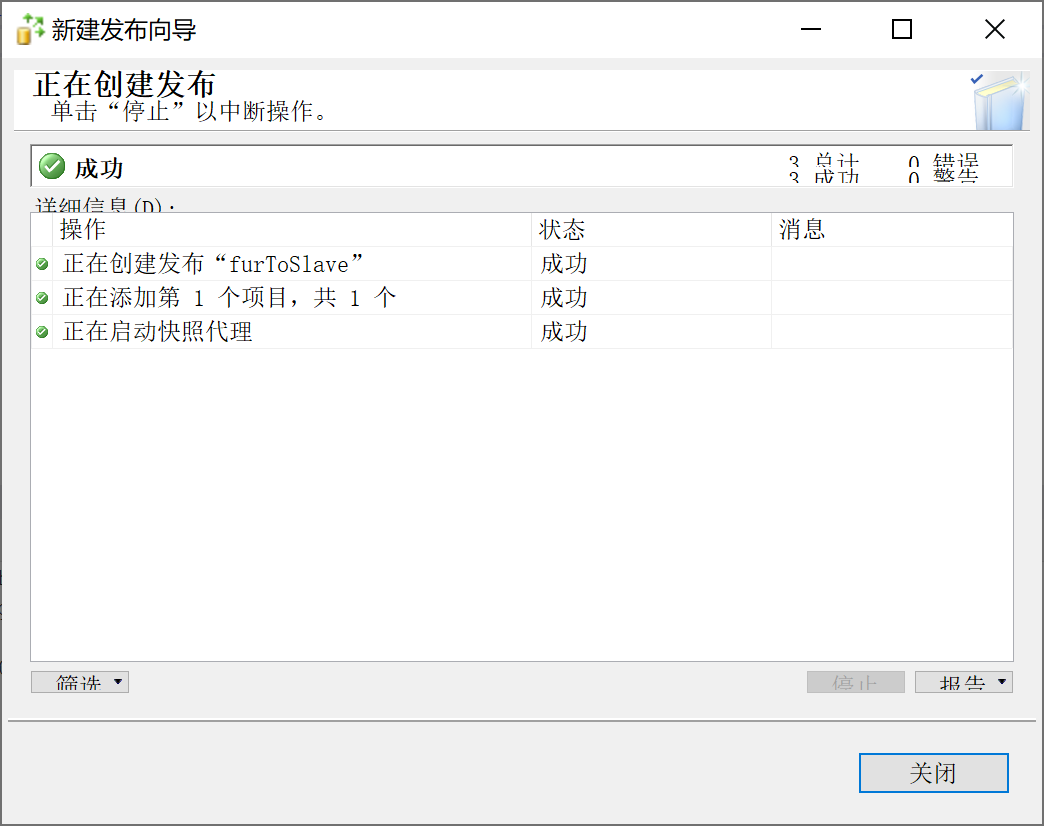
9.28.6 SqlServer 从库配置
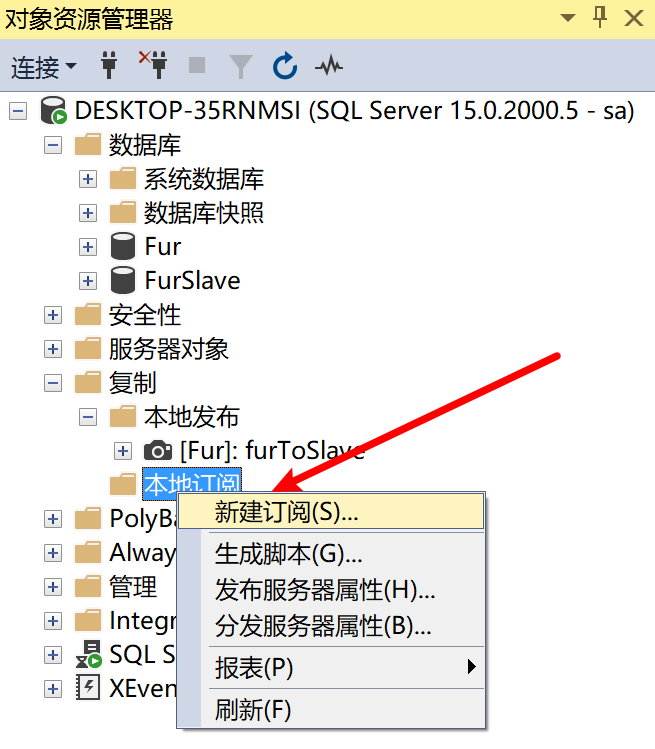
9.28.6.1 添加 本地订阅
9.28.6.2 选择 分发服务器
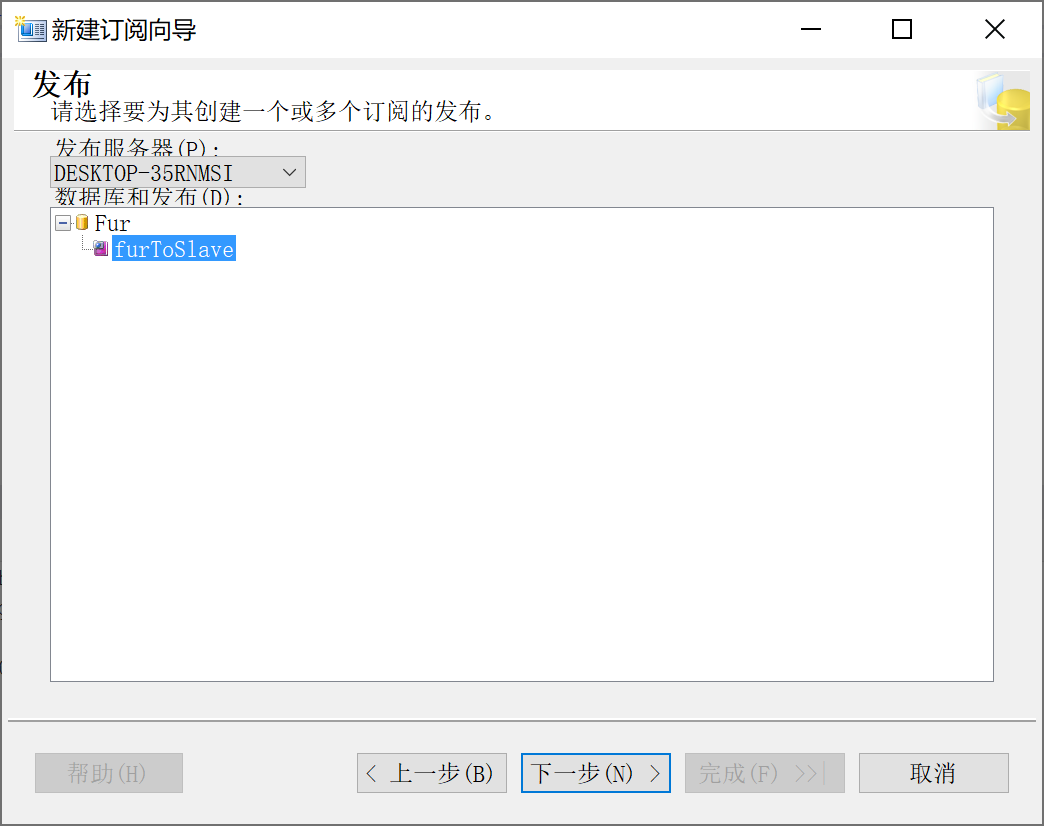
9.28.6.3 选择 分发代理位置
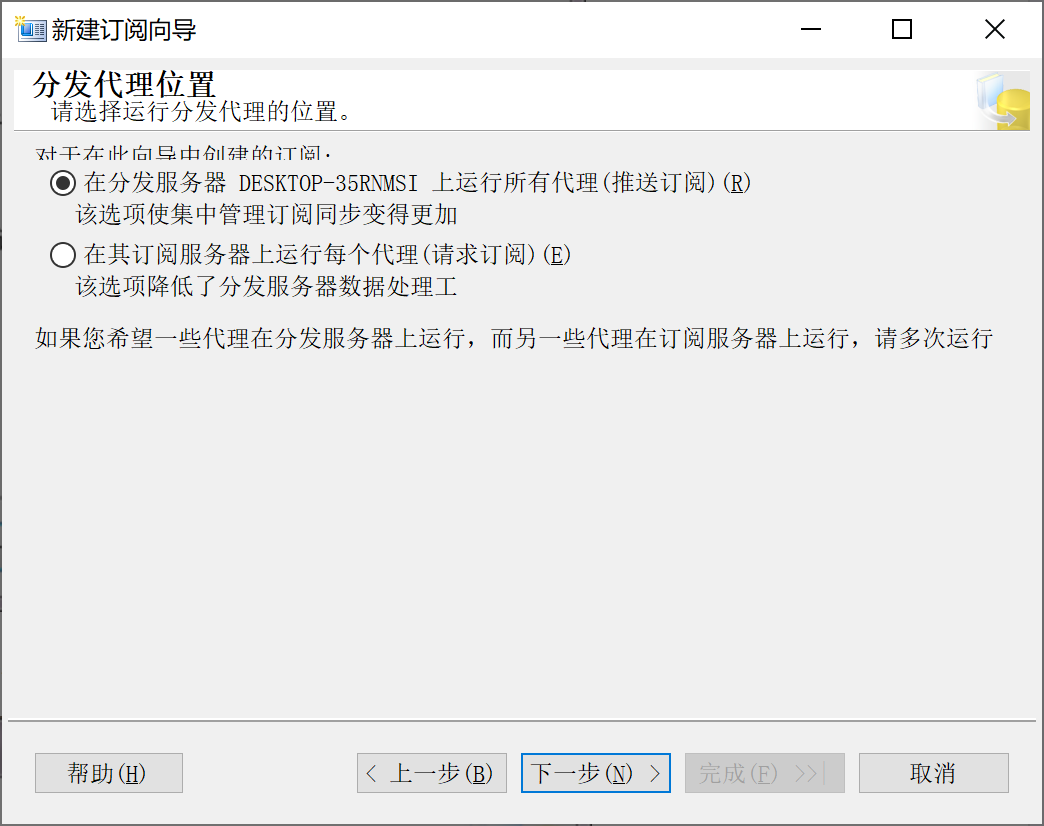
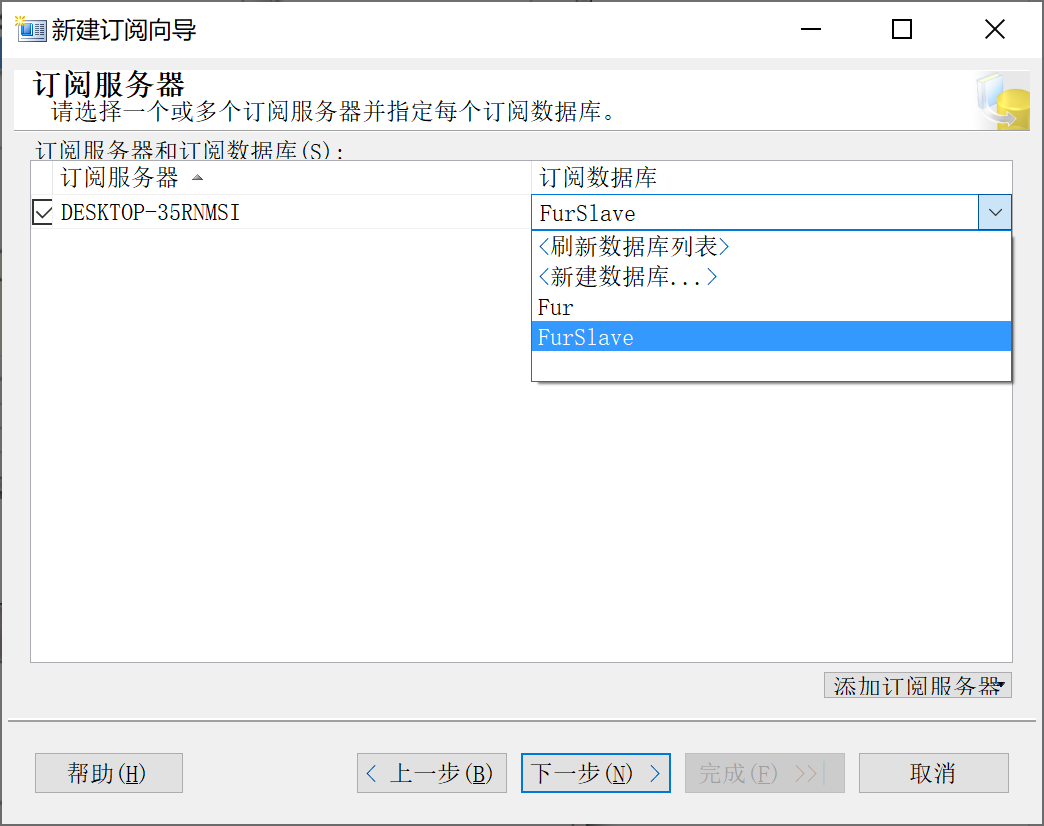
9.28.6.4 选择 订阅数据库
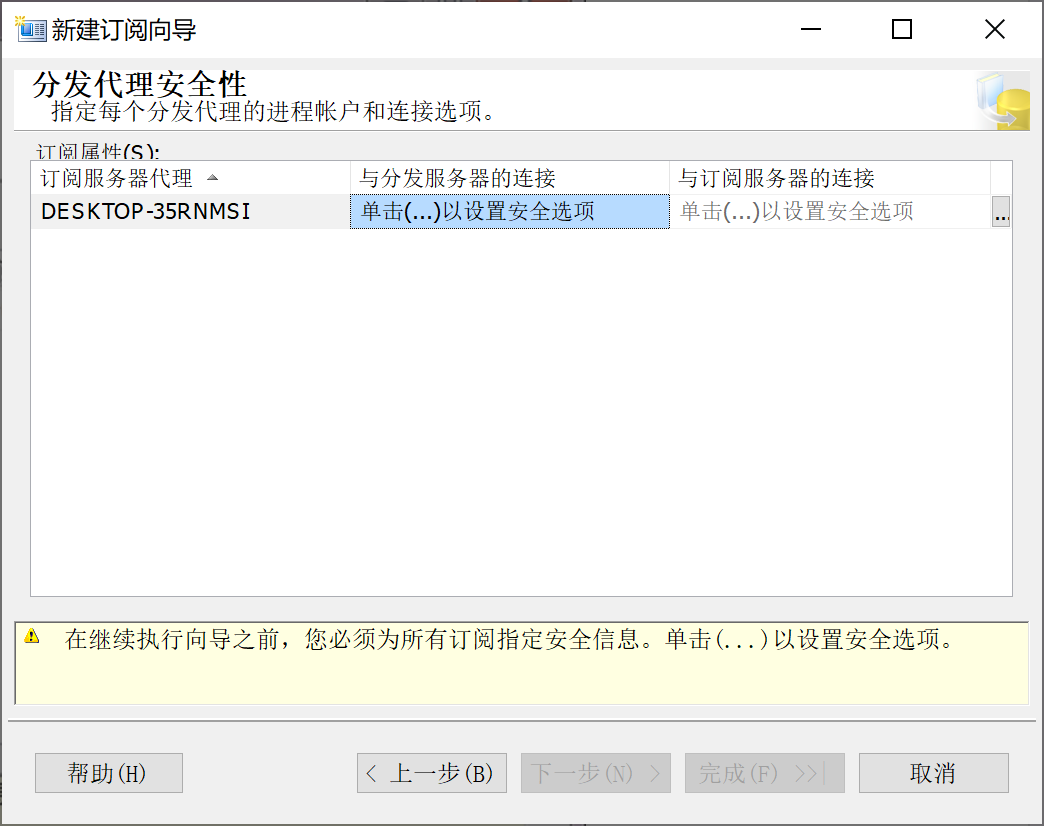
9.28.6.5 选择 分发安全设置
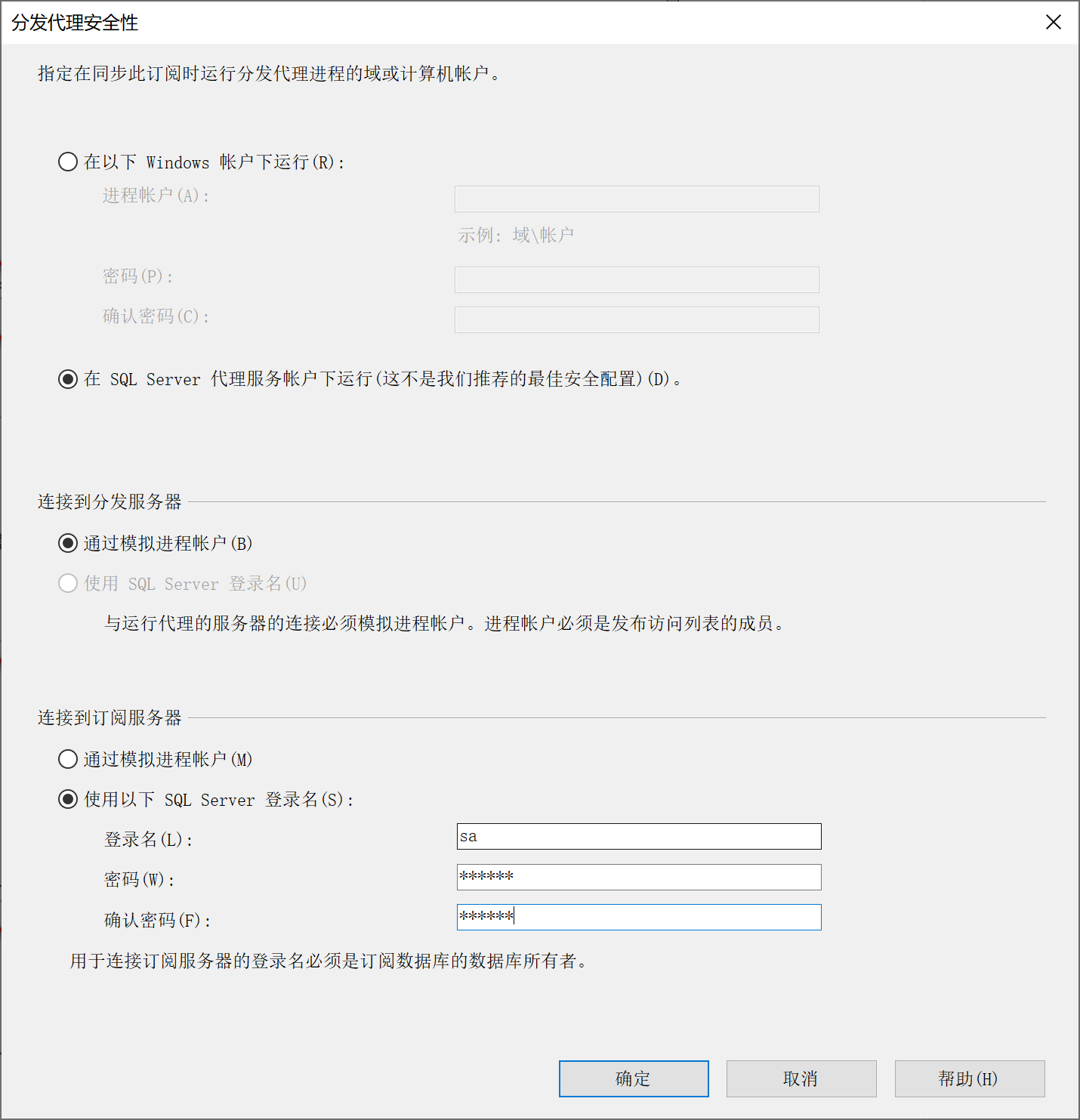
9.28.6.6 选择 同步计划
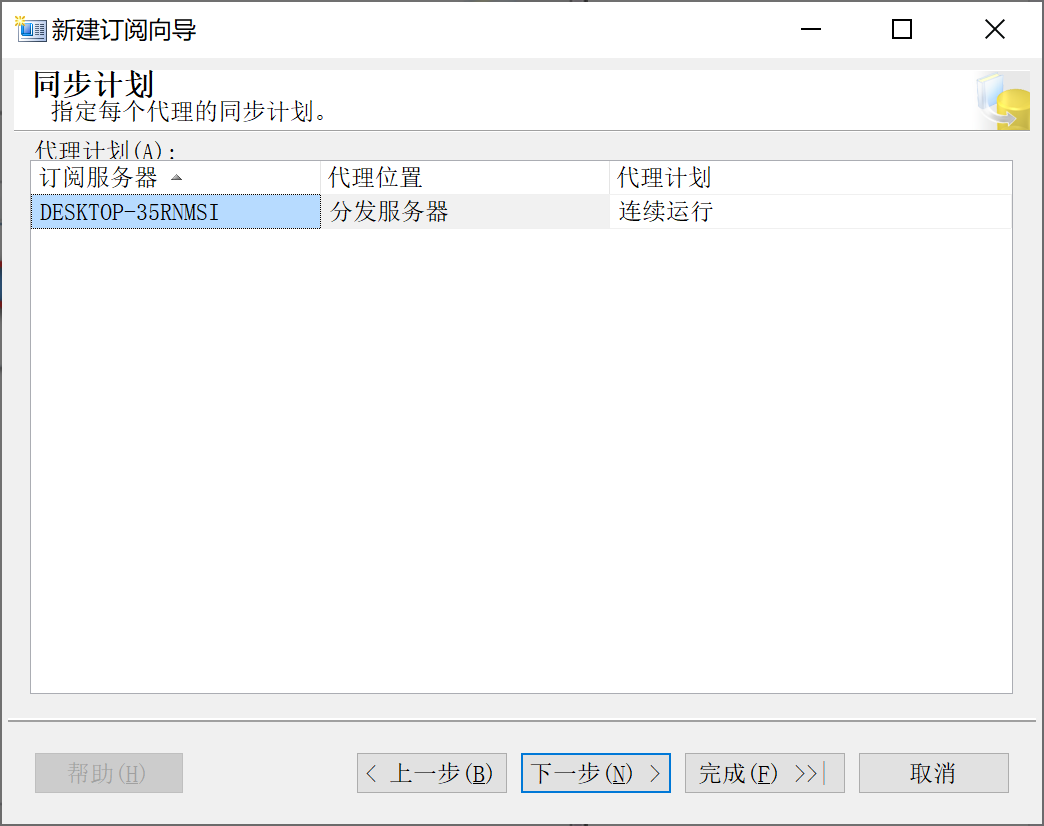
9.28.6.7 完成订阅
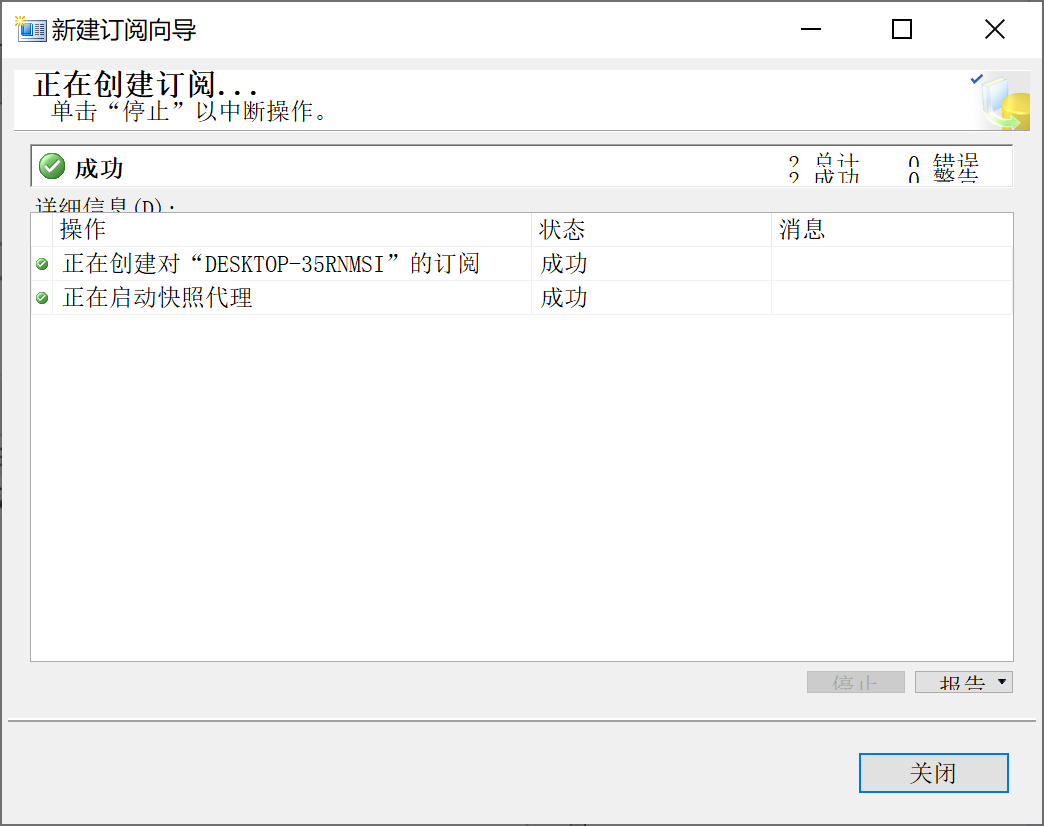
9.28.7 分发定义监视
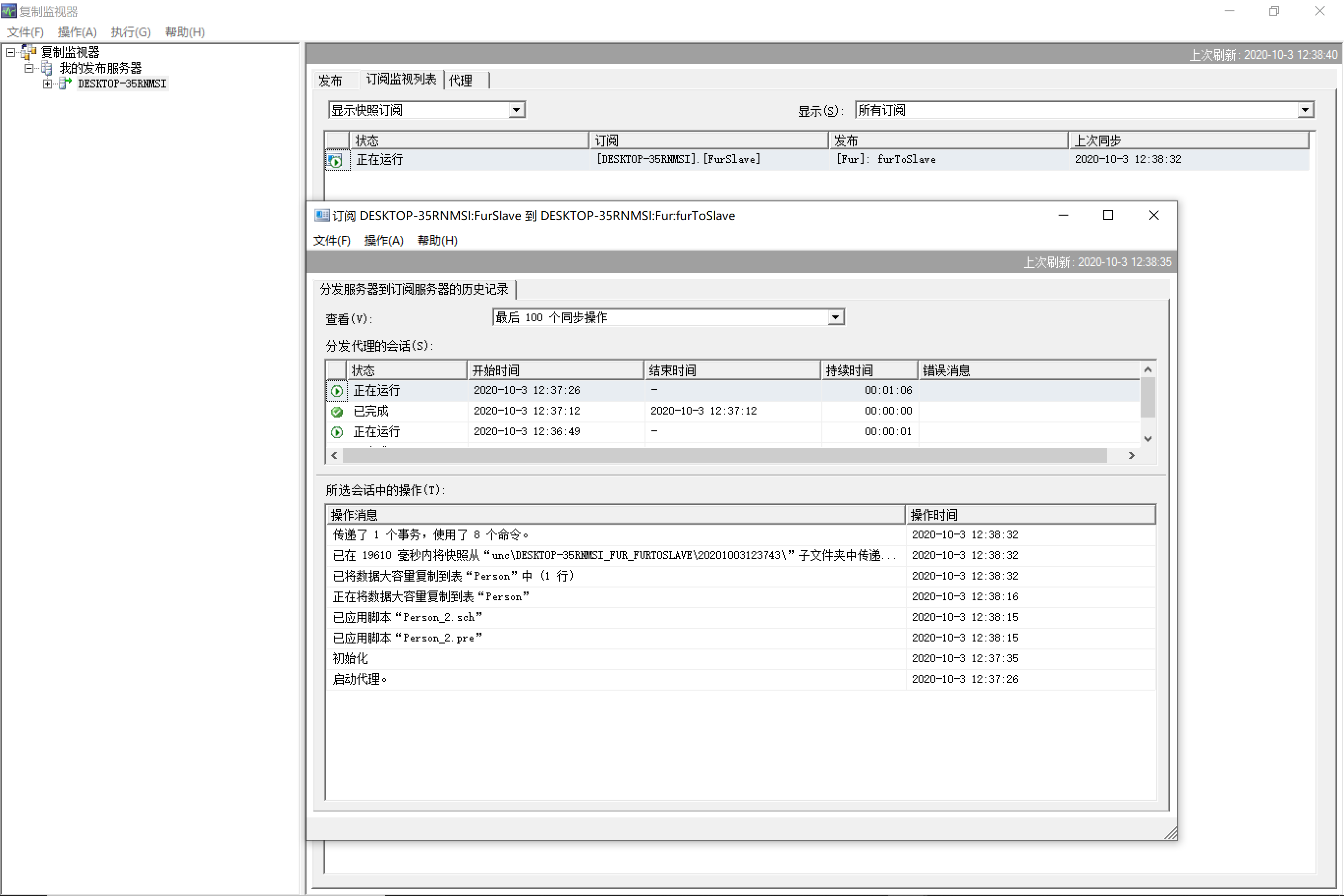
9.28.8 查看主从复制结果
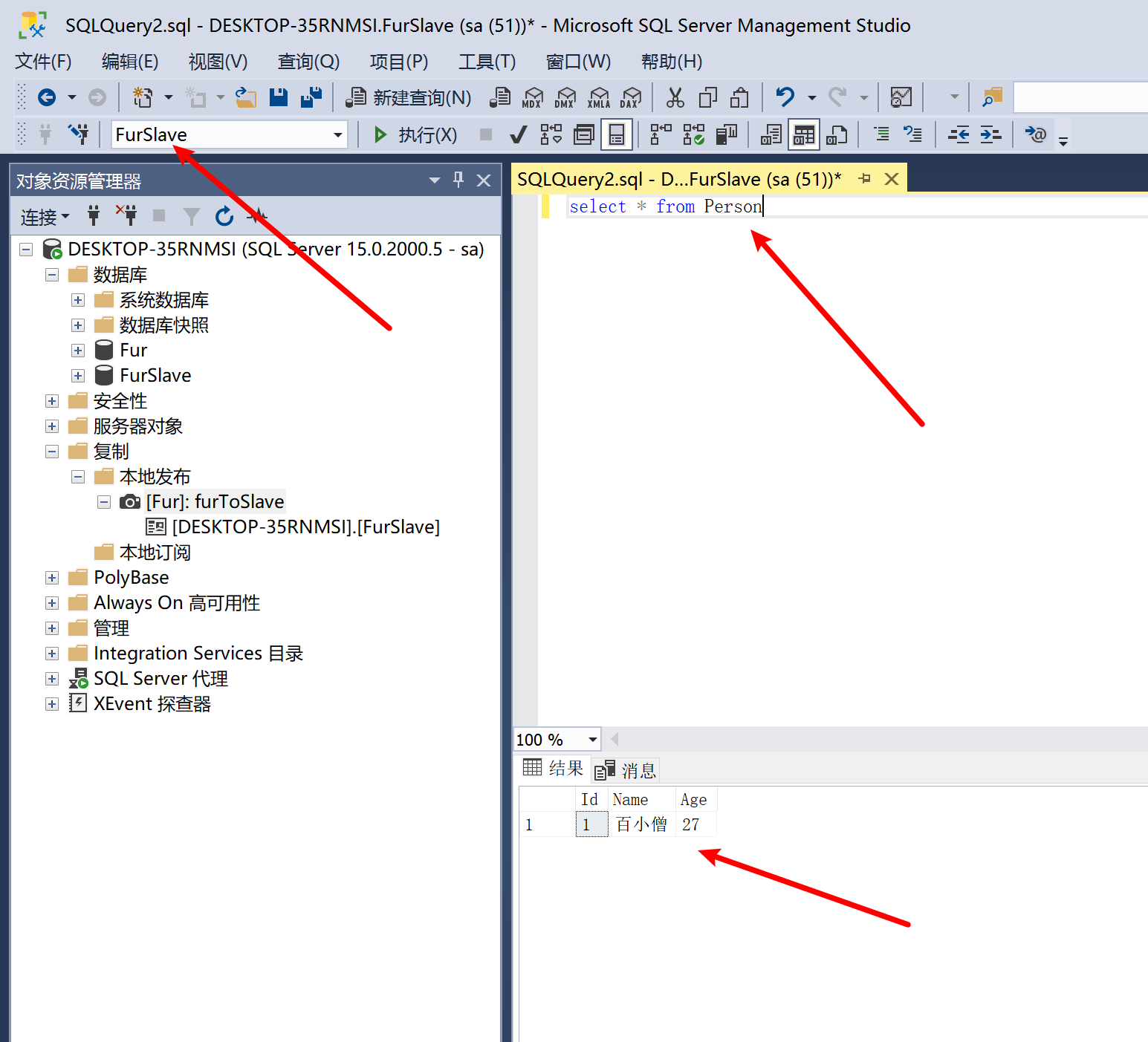
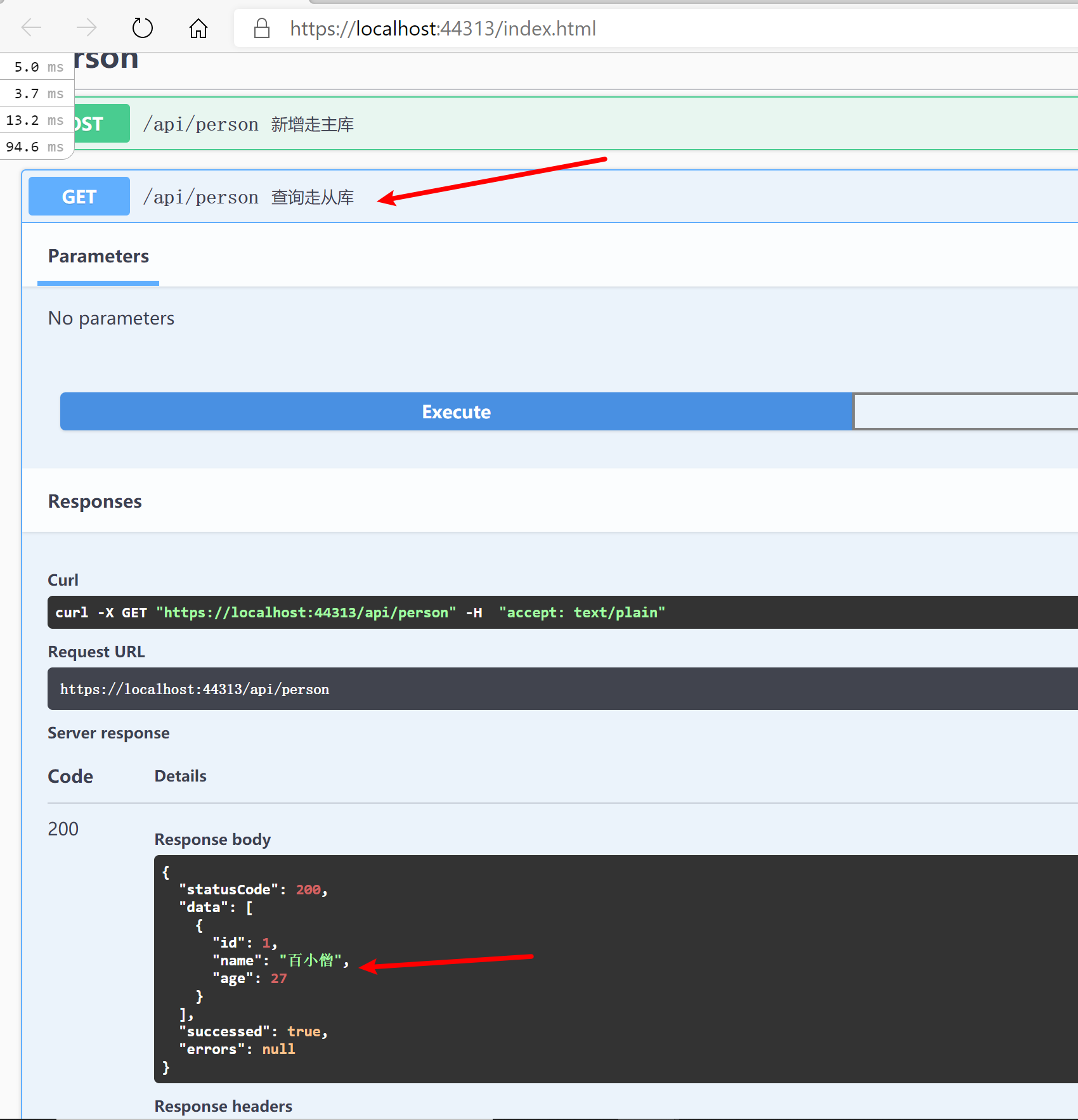
主从复制有一定迟延性,所以系统设计要有一定“容忍性"。
9.28.9 反馈与建议
给 Furion 提 Issue。
